What is a limit order?
A limit order, sometimes called a limit-entry order, is an instruction to your trading provider to open a trade when the market level reaches a better, preselected price. If you’re buying, ‘better’ means a lower price but if you’re selling, it means a higher price.
You can place a good-till-cancelled or good-till-date order – but selecting a price that’s better than the current price will always be a limit order. If the price you set is worse than the market price, it’s a stop order.
The bid price is the best price to sell at, and the ask price is the best price to buy at.
What’s the difference between a limit order and a limit?
While a limit order is a type of working order, a limit (also called a take-profit) is a risk management tool that you can attach to a trade to set a predetermined level to close your position if the market moves in your favour.
For example, for a long position on DBS Group Holdings shares, you can set a limit order by choosing a price level that’s lower than the market price. Your position will open automatically if the share price hits your chosen level or gaps beyond it. You can place a take-profit on a contract for difference (CFD) limit order, but it won’t come into effect until the price is reached and the trade is filled.
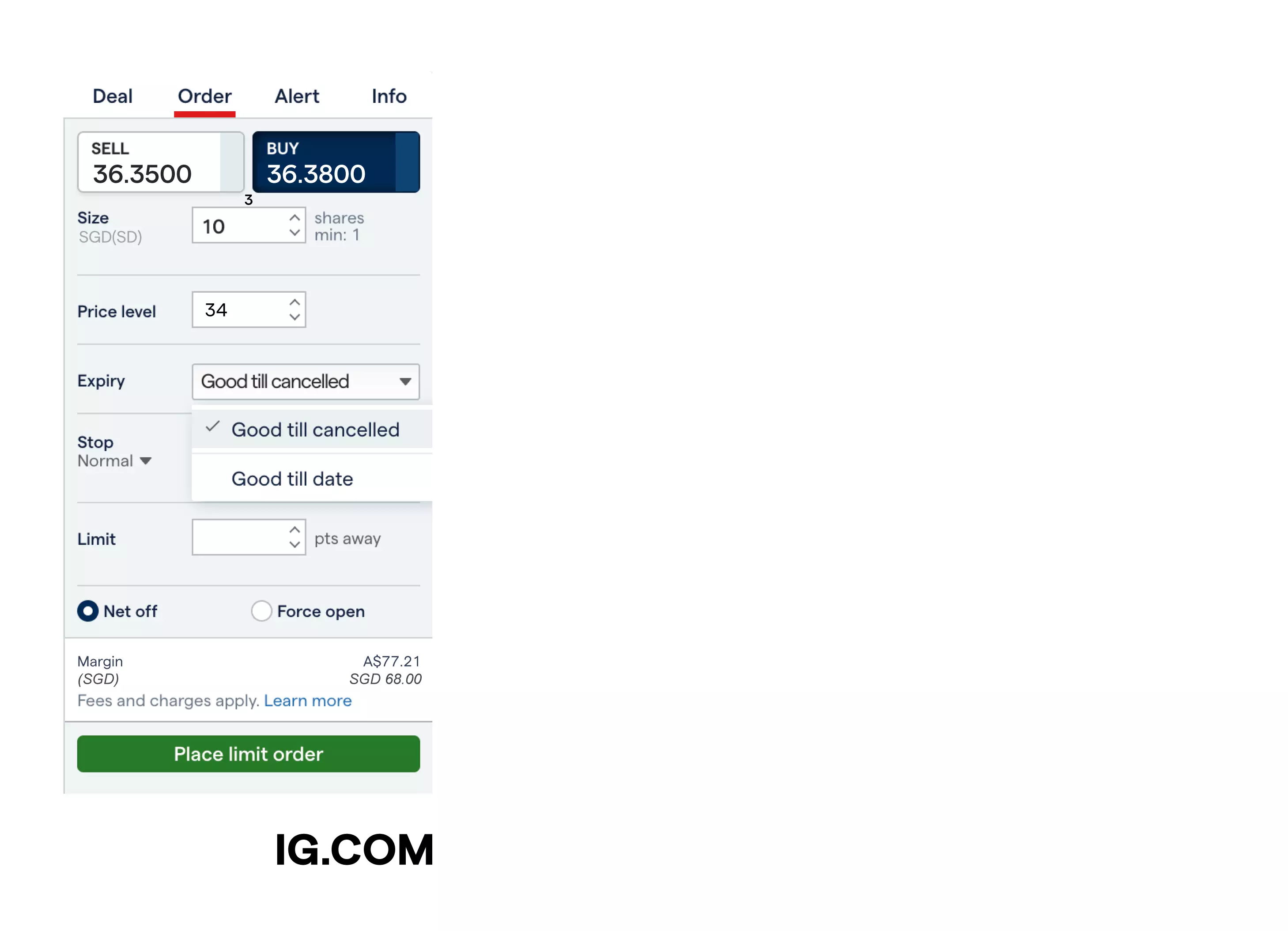
What’s the difference between a limit order and a market order?
The main difference between a limit order and a market order is the entry price level that you accept to open your position at.
A limit order is a type of working order – that’s set via the ‘Order’ tab of the deal ticket on our platform – to enter a position once a specific, more favourable price level has been reached.
A market order is an instruction to open a trade immediately, irrespective of the price (whether it’s at the same level you placed your order at, a more favourable price or a less favourable price). So, the trade will be opened at the best available market price, which could be worse than the price you see on the deal ticket. This means that your position could be subject to positive or negative slippage. A market order can be placed using the 'Deal' tab of the deal ticket on our platform. In summary, a limit-entry order is fill-later; a market order, on the other hand, is fill-now.
With limit and stop orders, your trade could be filled partially if your preferred price level is reached – this is based on liquidity, i.e. whether there are enough willing buyers or sellers to counter your position.1 You have to ‘accept partials’ in your settings.
With market orders, your trade will be opened at the full position size you set – liquidity and the size of the order will be taken into consideration.1
Learn more about the differences between a limit order and a market order
How does a limit order work?
Limit orders are designed to work automatically.1 This can be useful, especially in volatile markets when prices change suddenly and you don’t have time to manually open a trade during a short window of opportunity.
Note: if you’re buying, your limit order level will be below the current price. If you’re selling, your limit-entry order will be above the current price.
How to place a limit order
Open a trading account to get started, or practise on a free demo account
Conduct technical and fundamental analysis on the market you want to trade
Select the 'Order' tab on the deal ticket of the market you're trading on
Decide whether you’re going long or short
Put in your position size
Pick your price level – the ‘better’ price at which you want your limit entry to be triggered – and place your order (based on the opening price that you choose, our platform will show you whether it’s a stop or limit order on the ‘Place order’ button)
Choose between a ‘Good till cancelled’ limit entry, which will run until the predetermined price level is met (unless you cancel it), and a ‘Good till date’ order, which will close out automatically on a predetermined future day if the order isn’t executed
Click on the ‘Place limit order’ button
Your position will normally open automatically when the market hits your price level1
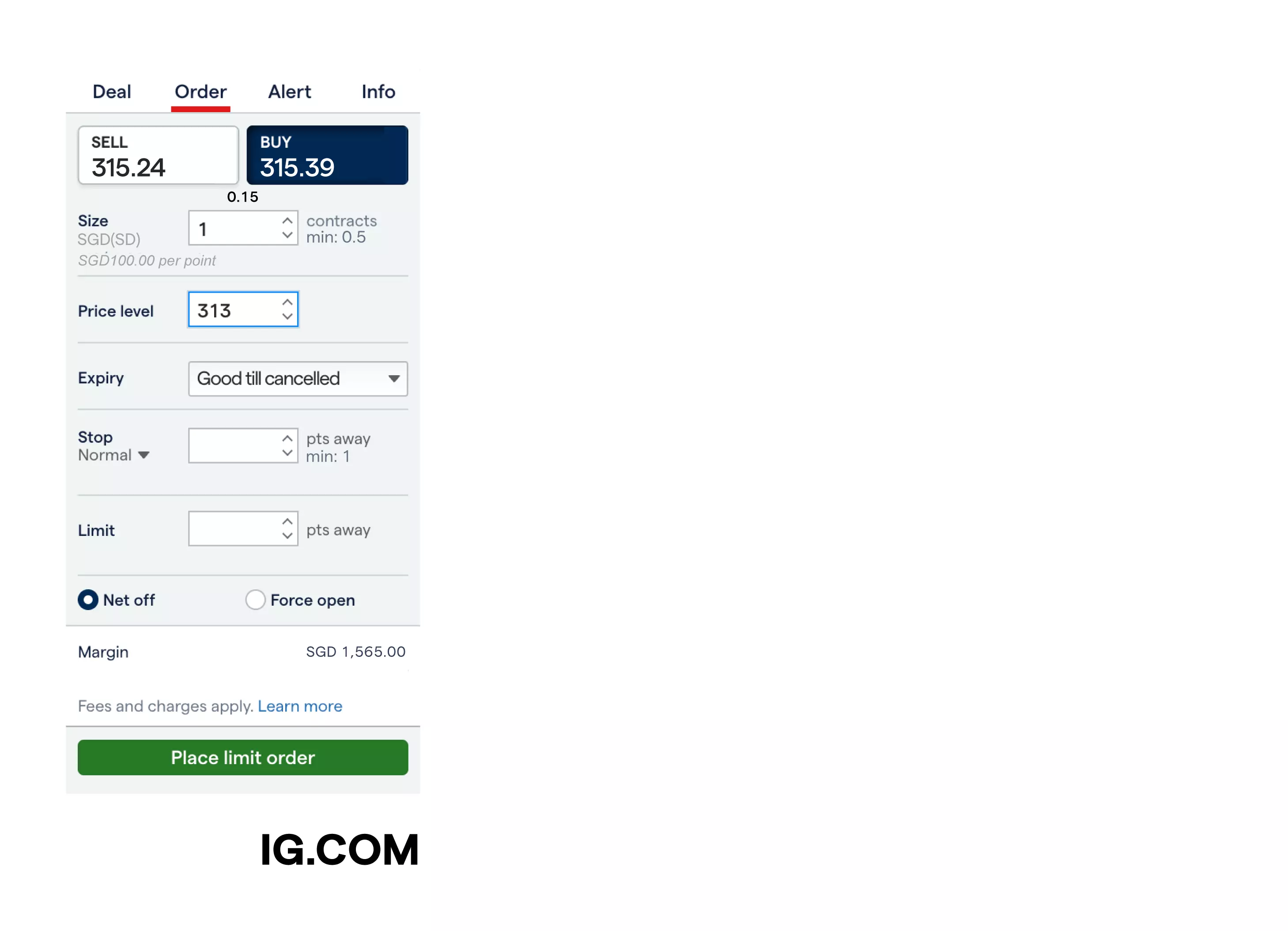
Example of a limit order
Let’s say you want to go short on Tesla shares and place a limit-entry order. You’ve conducted your own analysis and believe that Tesla shares will likely fall soon. Your prediction is that this will happen when the share price, which is currently at 257.50, hits 259.00.
So, you decide to open a CFD trade and set up a limit-entry order to sell (go short on) 10 Tesla shares when the price hits 259.00. If Tesla’s share price rises to 259.00, you’ll have an open position as your limit-entry order will be executed.
Suppose you also placed a limit (take-profit) at 249.00 so that your position will close out profitable if the market reaches this level. If your take-profit is triggered, you’d make a profit of $100.00 (10 x [259.00 – 249.00]). However, if the share price rallies to 269.00, you’d make a loss of $100.00 (10 x [259.00 – 269.00]).2
Benefits and risks of a limit order
Benefits of using limit orders
Limit orders are designed to work automatically –1 this can be useful as you don’t have to open positions manually at your preferred price, especially in volatile markets when prices change rapidly
In the case of very volatile markets, this could even lead to a phenomenon called ‘positive slippage’ – where the market suddenly moves beyond your set price, fulfilling your order at an even better price
Risks of using limit orders
There’s the chance that a position may never be opened, which could affect your trading strategy, because a limit order is ‘your price or better’
Limit orders don't guarantee a fill at your chosen price. If the market moves in a volatile way through your price, it may gap up or down and the pre-determined price may be missed by a large amount (slippage)
Limit orders don’t protect against losses when the market moves against your position – for that, you’ll need a stop-loss. However, a limit order could act as a stop loss if you set a working order to ‘net off’.3 In fact, that’s how you’d do it on a share trading account with us. While this is also possible on a CFD trading account with us, it’s generally not an efficient way to go about it as you could place a stop loss to a position instead of opening a separate position, unless the aim is to partially close an existing position





