
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Solayer extends staking beyond core validators, increasing security and earning potential for SOL and LST holders.
Restaking strengthens decentralization by distributing stake across additional security layers and services.
Solayer’s LAYER token is fundamental to its restaking ecosystem, supporting security, governance, validator incentives, and transaction fees.
Restaking is emerging as a key trend in Solana and beyond, offering new ways to enhance blockchain security and staking rewards.
Solana’s staking landscape is changing, and restaking is at the forefront of this transformation.
Traditional staking allows users to secure the network while earning rewards, but restaking introduces additional security layers and enhances decentralization.
Restaking allows stakers use their assets to support multiple proof-of-stake (PoS) networks at the same time, increasing security while earning more rewards.
This approach enables SOL and liquid staking token (LST) holders to extend their staking beyond core validators, supporting a broader range of network functions.
This article explores Solayer (LAYER), a restaking protocol designed to strengthen Solana’s security and scalability. It covers how Solayer’s restaking mechanism works, the role of the LAYER token, validator selection, risk management, and earning opportunities.
What Is Solayer (LAYER)?
Staking is locking up cryptocurrency assets to support blockchain operations, such as transaction validation and earning rewards. Solayer draws inspiration from mechanisms like Ethereum’s EigenLayer, bringing the concept of restaking to Solana.
Solayer is a restaking protocol that allows SOL holders to extend the utility of their staked assets beyond the core validators that maintain Solana’s integrity. By enabling restaking, Solayer facilitates the secure delegation of SOL to Actively Validated Services (AVSs) like oracles and bridges within the ecosystem, improving their security and reliability, which in turn strengthens on-chain applications.
This redistribution of staked assets enhances overall network security and decentralization while providing users with additional opportunities to earn rewards.
How Does Solayer’s Restaking Mechanism Work?
Solayer integrates with Solana’s Proof-of-History (PoH) to ensure restaking does not interfere with network finality—the point at which a transaction is confirmed and cannot be reversed. PoH timestamps transactions cryptographically, allowing validators to process them in a fixed order. Solayer redistributes staked SOL without affecting transaction speed or consensus integrity.
Restaking Process
Users stake SOL or LSTs through Solayer, locking assets into smart contracts that delegate beyond Solana’s core validator.
Validators spread staked SOL and LSTs, which are tokens received when SOL is staked through LSTs like Marinade (mSOL), across different security layers and projects that support the network, such as oracles, cross-chain bridges, and execution layers. These services rely on staked assets to improve reliability and security.
Smart contracts adjust delegation based on security needs and network activity, ensuring that SOL and LSTs are placed where it strengthens the system while maximizing efficiency.
By allowing SOL or LSTs to secure multiple services, Solayer reinforces the network and expands earning opportunities for users.
Reward Distribution
Stakers earn rewards in sSOL, representing their staked SOL within the Solayer ecosystem. These rewards come from transaction fees, validator incentives, and network participation bonuses.
Restaking expands validator roles, allowing them to secure multiple decentralized services while earning additional incentives.
Rewards ensure a balance between security and incentives, reinforcing network resilience and encouraging long-term participation.
eSOL remains liquid, enabling users to reinvest in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or withdraw their underlying SOL or LSTs when unstaking.
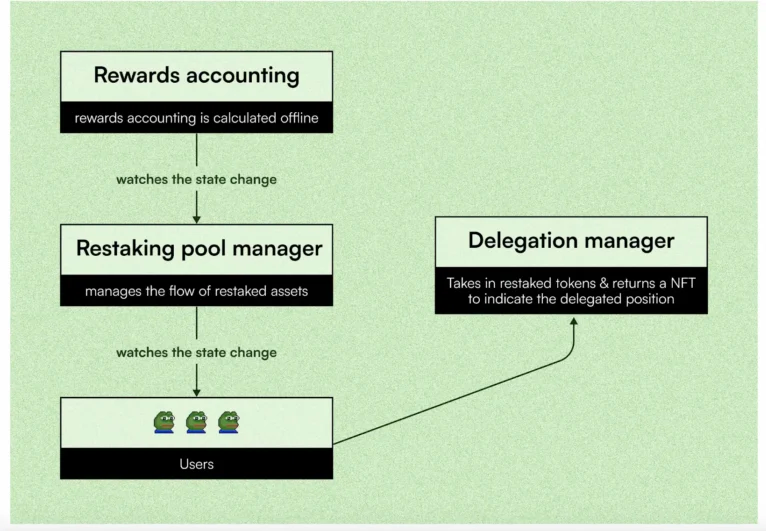
Smart Contract Interactions and Validator Processes
Solayer automates staking delegation and reward distribution through smart contracts, ensuring efficient and secure allocation of SOL.
Validator selection: Solayer’s smart contracts allocate SOL based on validator’s reputation, performance, and security contributions.
Automated restaking: Smart contracts dynamically adjust delegation, optimizing security without manual intervention.
Risk management: The protocol monitors validators and reallocates SOL if security concerns arise.
What Is the Layer Token and How Does It Work?
LAYER is Solayer’s native token and the foundation of its restaking ecosystem. It supports network security, governance, and validator incentives while covering transaction fees.
Utility: LAYER powers governance, validator rewards, and transaction fees. It aligns incentives and secures the restaking process.
Token distribution: It defines total supply, initial allocations (team, investors, rewards), and staking mechanisms. A portion supports validators, ecosystem growth, and protocol development.
Governance: It also grants holders voting power over network upgrades, security policies, and staking rules, ensuring decentralization and adaptability.
Ideally, a structured tokenomics model reinforces security, incentivizes participation, and sustains long-term network stability.
Solayer Restaking: Risks and Benefits
Users should consider both risks and benefits before participating in Solayer’s restaking mechanism.
Risks of Restaking With Solayer
Smart contract risks: Automated contracts handle staking and delegation, but vulnerabilities could lead to fund losses.
Validator penalties: Poor performance or malicious actions can result in slashing, which removes a portion of a validator’s staked SOL as a penalty.
AVS exposure: Users who restake SOL to AVSs take on the risks of these services, including security breaches, downtime, or smart contract failures that may impact rewards.
Liquidity fluctuations: sSOL remains liquid, but market conditions and user demand determine its value and tradeability.
Variable rewards: Returns are not fixed and depend on validator efficiency, network activity, and AVS performance.
Unstaking delays: Restaking involves a withdrawal period, typically lasting a few days and tied to Solana’s epoch duration, during which users cannot access their SOL.
Protocol uncertainty: As a new platform, Solayer faces risks tied to adoption, security updates, and unforeseen technical issues.
Benefits of Restaking With Solayer
Higher rewards: Users earn additional incentives by securing multiple services beyond Solana’s core validators.
Enhanced security: By redistributing staked SOL across different validation layers, Solayer reduces attack risks and strengthens network integrity.
Increased decentralization: Restaking expands security contributions to AVSs, reducing reliance on a small group of validators.
Liquidity through sSOL: Users receive sSOL, which they can use for additional earning opportunities within DeFi applications.
Automated staking management: Smart contracts adjust delegation dynamically, eliminating the need for manual adjustments.
Flexible staking options: Users can allocate SOL across multiple security layers, diversifying their staking strategy.
How Does Solayer Compare To Other Restaking Mechanisms?
Solayer competes with other restaking mechanisms on Solana, such as Jito and Picasso, each offering a different approach to securing the network and maximizing staking rewards.
While Solayer prioritizes native integration and validator coordination, Jito focuses on staking efficiency, and Picasso enables cross-chain restaking. The table below highlights their key differences:
| Feature | Solayer | Jito | Picasso |
| Native integration | Built on Solana | Built on Solana | Cross-chain |
| Restaking mechanism | Restakes SOL & LST | Restakes SOL | Restakes SOL & LST |
| Shared validator network | Yes | No | No |
| Restaking service | Secures multiple networks | Boosts staking efficiency | Secures AVSs |
| Economic impact | Optimizes validator rewards | Improves validator incentives | Supports multiple chains |
Stakers use Jito primarily for native SOL restaking, but Jito also issues JitoSOL, an LST that captures Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) rewards—profits from optimizing transaction order and execution—to boost returns.
While Jito’s restaking service does not restake other LSTs as Solayer does, stakers can use JitoSOL within Solayer’s ecosystem for additional restaking opportunities. This lets stakers benefit from Jito’s MEV-enhanced staking while securing multiple services through Solayer.
Picasso, on the other hand, lets stakers use SOL and liquid-staked derivatives to secure AVSs across multiple blockchains through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. This expands staking utility beyond Solana and reinforces security across different networks.
Conclusion
Solayer (LAYER) introduces a restaking model that extends SOL staking beyond core validators, enhancing security, decentralization, and staking efficiency within the Solana ecosystem. By enabling users to stake SOL and LSTs across multiple security layers, Solayer strengthens the network while offering additional earning opportunities.
The LAYER token supports governance, validator incentives, and transaction fees, ensuring a sustainable staking ecosystem. Smart contracts manage automated delegation, validator selection, and risk mitigation, optimizing security without manual intervention.
Restaking continues to expand within Solana, providing new ways to secure decentralized services. As protocols refine their staking mechanisms, Solayer’s approach to shared validator networks and economic security will shape Solana’s ecosystem.





