As the blockchain world grows, so does the number of independent networks. Ethereum, Solana, Sui, and many others all offer different advantages — but they don’t naturally speak the same language. This lack of communication between blockchains creates barriers for developers and users. It limits how apps work across chains, and how easily assets or data can move between them.
That’s where interoperability protocols come in. These protocols aim to bridge the gap between blockchains by allowing them to exchange information and interact. One of the latest projects tackling this challenge is Hyperlane — a protocol built to connect different chains through a messaging layer. In this article, we’ll explore what Hyperlane is, how it works, the HYPER tokenomics, and how to buy Hyperlane (HYPER).
What Is Hyperlane (HYPER)?

Hyperlane , or HYPER, is a cross-chain interoperability protocol founded in 2022 by Jon Kol, Asa Oines, and Nam Chu Hoai. It was created to solve one of the biggest challenges in blockchain technology: enabling seamless communication between different blockchain networks. Hyperlane allows smart contracts to send messages, trigger functions, and move data across chains — not just tokens. This makes it possible to build decentralized applications (dApps) that operate across multiple ecosystems.
Unlike traditional blockchain bridges, Hyperlane is permissionless and modular. Developers can deploy the protocol on over 140 blockchains — whether it’s Arbitrum, Solana, Cosmos SDK chains, or newer rollups — without needing approval. It supports interoperability between Layer 1, Layer 2, and app-specific chains, giving projects more flexibility in how they expand and connect their services.
A key feature of Hyperlane is its use of Interchain Security Modules (ISMs). These customizable smart contracts verify the origin and authenticity of cross-chain messages. ISMs can be configured, combined, or custom-built to fit the security needs of different applications. This modular approach to blockchain security makes Hyperlane a flexible foundation for building cross-chain DeFi platforms, NFT projects, DAO governance tools, and more.
How Hyperlane Works
Hyperlane is designed to help blockchains send messages to each other in a reliable and flexible way. It breaks the process into two main parts: transport (how messages move between chains) and security (how those messages are verified). This separation gives developers more control and makes the protocol easier to use across different blockchain environments.
1. Mailbox Contracts
Every blockchain that supports Hyperlane has a Mailbox smart contract. This contract is the entry and exit point for all interchain communication.
● When a smart contract on Chain A wants to send a message to Chain B, it uses the Mailbox’s dispatch function. This message is then added to a Merkle tree — a special data structure that helps prove the message was really created.
● On the receiving chain, the Mailbox’s process function is called to complete the message delivery. The handle function sends the message to the right application.
Mailbox contracts are the core of Hyperlane’s message-passing system. Every chain in the network has one.
2. Relayers
Relayers are off-chain services that watch for new messages in Mailboxes.
● When a message is created on the origin chain, a relayer picks it up.
● It then gathers metadata — including any required validator signatures — and sends the message to the destination chain’s Mailbox contract.
● Relayers are not trusted by default. They don’t check if a message is valid — they just help transport it.
Anyone can run a relayer, which keeps the network open and decentralized.
3. Interchain Security Modules (ISMs)
ISMs are smart contracts that protect the system by verifying cross-chain messages.
● They check whether a message that arrived on the destination chain was really sent from the origin chain.
● Hyperlane gives developers full control here. They can use simple default ISMs, select pre-made versions with custom settings, or build entirely custom ISMs based on their app’s needs.
This modular approach means each project can choose how strong or flexible its security needs to be.
4. Validators
Validators play a key role in verifying messages.
● They watch the Mailbox on each chain and sign Merkle roots — cryptographic summaries of all recent messages.
● Their digital signatures act as proof that a message was included in a valid checkpoint.
Unlike many protocols, Hyperlane does not rely on a single validator set. Each app can choose its own group of validators based on how much trust and decentralization it wants.
5. Interchain Gas Payments (IGP)
Sending messages across chains costs gas — not just on the origin chain, but on the destination chain too.
● Hyperlane makes this easier with Interchain Gas Paymaster (IGP) contracts.
● These smart contracts let users prepay gas fees on the origin chain. The payment is then used to cover costs on the destination chain when the message is delivered.
This system improves the user experience and ensures that relayers can deliver messages without delays.
6. Warp Routes
Warp Routes are Hyperlane’s built-in token bridging solution.
● They support moving ERC-20 tokens, NFTs, and native assets between chains.
● The token on the source chain is locked, and a wrapped version is minted on the destination chain. When tokens are sent back, the wrapped version is burned and the original is unlocked.
Warp Routes use the same messaging and verification system as the rest of Hyperlane, which keeps the design consistent and secure.
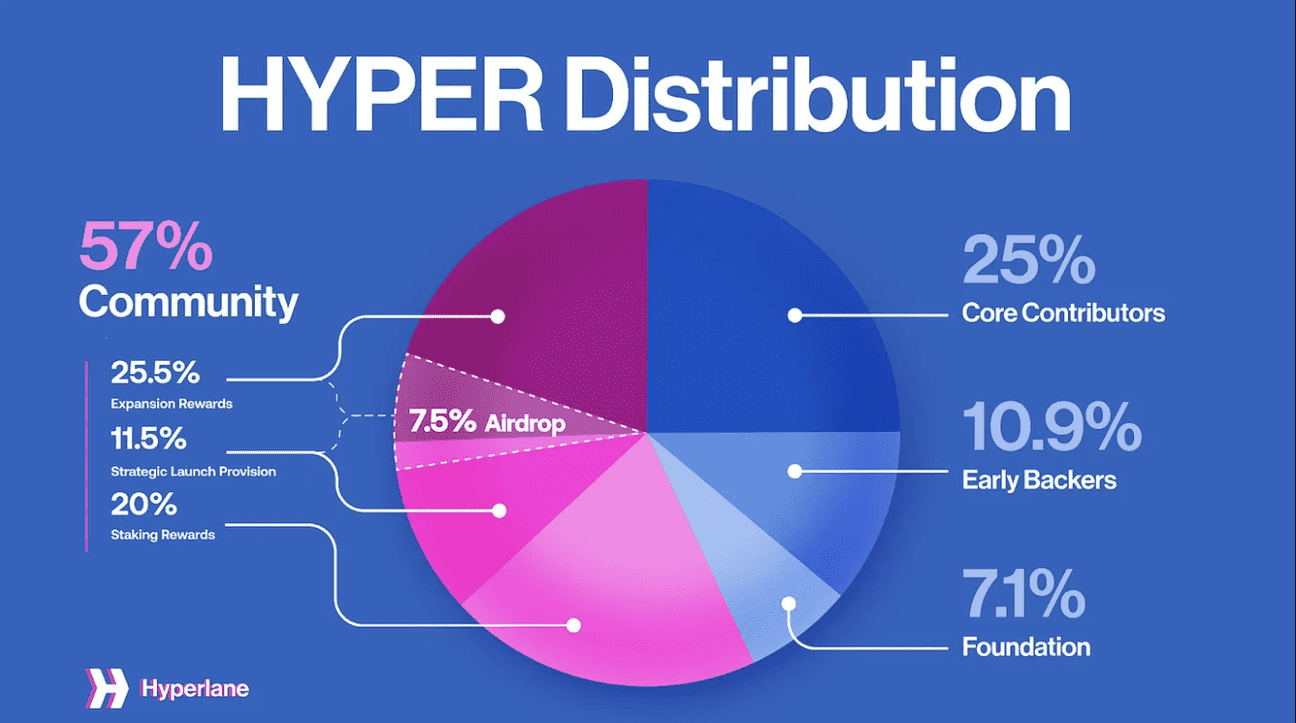
What Is HYPER Tokenomics?
HYPER is the native token of the Hyperlane protocol. It plays a central role in the protocol’s economic and security system. HYPER is used for staking, validator selection, and rewarding users who help run and use the network. The token exists across multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism. HYPER has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens, which will be fully released over a 25-year period. At launch, 177.7 million HYPER tokens are in circulation.
When users stake HYPER into the Symbiotic vault, they receive a liquid staking token called stHYPER. This token represents their staked amount and can be held or used to earn staking rewards. The longer users hold stHYPER without moving or withdrawing it, the higher their HyperStreak bonus — a reward multiplier based on consistency and loyalty. Unstaking requires waiting through an epoch cycle, typically lasting about 30–60 days.
Validators who secure message verification on supported chains are also selected based on their HYPER stake. Those included in a chain’s default Interchain Security Module (ISM) earn validator rewards as a commission from the staking pool. To maintain trust, Hyperlane includes a slashing mechanism that penalizes validators who act dishonestly or submit invalid data, which helps protect message integrity across chains.
HYPER also powers the network’s reward system. Stakers earn regular rewards, validators receive commissions, and users who send messages between chains may qualify for Expansion Rewards. Overall, HYPER tokenomics are designed to align incentives between users, validators, and developers — encouraging long-term participation and helping to secure the protocol as it grows.
Is Hyperlane Safe?
Hyperlane takes a flexible approach to security by allowing developers to decide how messages between blockchains are verified. This is done through Interchain Security Modules (ISMs) — smart contracts that act as custom security layers. Some apps might use simple setups, while others can build multi-layered verification systems with validator signatures or multi-signature approval. It’s not one-size-fits-all, which is powerful, but it also means the security depends on how well each app is configured.
To keep validators honest, Hyperlane uses a slashing mechanism that penalizes anyone who tries to cheat the system. If a validator signs an invalid message, they risk losing some of their staked HYPER. Combined with open participation for relayers and validators, and a clear path toward decentralized enforcement, Hyperlane provides the tools for strong security — but leaves the final decisions in the hands of the builders.
How to Buy Hyperlane (HYPER)?
If you're interested in adding HYPER to your portfolio, good news — it's now easier than ever to access. Hyperlane (HYPER) is officially listed in the Bitget Innovation and Web3 Zone.
Conclusion
Hyperlane introduces a flexible and open way for blockchains to communicate — not just through token transfers, but through messages that can carry data, instructions, and real-time interactions. Its modular architecture, permissionless deployment, and customizable security make it a powerful tool for developers building in a multi-chain world.
As the blockchain space grows more complex, the need for seamless cross-chain infrastructure becomes more urgent. Hyperlane addresses this need by making interoperability accessible and adaptable. The technology is here — the choice now rests with the builders.





