
New Bitcoin Layer 2 protocols are emerging to expand Bitcoin’s use cases and boost its scalability. The Spark Protocol is one of the most exciting entrants in the Layer 2 space, bringing together some of the best features of other Layer 2s in one protocol.
This guide will walk you through what the Spark Protocol is, how it works, and what it brings to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
TL;DR
What Is the Spark Protocol?
Spark is an open-source Layer 2 protocol designed to give Bitcoin high transaction performance and the capacity to support stablecoins and tokens.
Developed by Lightspark, it’s built on statechain technology that integrates atomic swaps, Lightning compatibility, and certain aspects of ARK, another L2 scaling solution.
Through the use of these technologies, Spark users can transfer value on top of Bitcoin without having to move the blockchain’s underlying assets each time a transaction takes place. At the same time, it reduces congestion on the Bitcoin network, drastically lowers transaction fees, and is non-custodial.
The Spark protocol is designed to support the issuance of stablecoins and tokens natively on the Bitcoin network. This is possible through the use of various technical solutions, including Taproot Assets and RGB (the ‘Really Good for Bitcoin’ smart contract system).
How Does Spark Work?
Spark operates as a distributed ledger on top of Bitcoin and enables you to move your BTC into a shared deposit address co-signed by you and Spark Operators (SOs), essentially nodes on a P2P network. From there, the BTC becomes a ‘leaf,’ or a virtual representation of a UTXO within Spark, which can be transferred instantly between users.
Statechain Technology
Spark relies on the statechain model, which enables off-chain transfer of value ownership without moving the underlying assets on-chain whenever the transaction happens. These off-chain transfers are coordinated by SOs and secured with threshold signature schemes, and allow users to exit unilaterally at any time.
Shared Signing Protocol
To utilize Spark, you deposit some BTC into a shared address jointly controlled by you and the Spark Entity (SE). The SE comprises multiple SOs who work together to enable ownership transfers and maintain liveliness. Using atomic swaps, Spark is linked to the Lightning Network, and seamless exits are enabled.
On-Chain vs. Off-Chain Representation
Though the BTC stays on-chain, all activity within Spark takes place off-chain. The UTXO is never moved except when you exit. This model avoids fees and delays, offering near-instant settlement with little on-chain footprint until necessary.
Key Features of Spark
Spark isn’t just another scaling solution. It’s an overhaul of Bitcoin transactions for real-world usage at scale. From near-zero fees and instant settlement to support for Lightning, stablecoins, and always-open exits, Spark delivers a suite of features that address the existing obstacles to Bitcoin’s usability and wider adoption.
Here’s a breakdown of the protocol’s most important capabilities:
Instant transactions: Off-chain ownership transfers happen in real time, letting you move BTC and other assets on Spark in less than a second.
Extremely low fees: At time of writing, no on-chain interaction means no fees on Spark and exceptionally low costs on Lightning and Bitcoin.
Self-custodial: Users maintain control over keys at all times and can always exit. Your keys, your coins.
Lightning-compatibility: Integrates with LN for seamless cross-network payments, with the need for no nodes or channels.
Tokens on Bitcoin: Supports easy issuance, transfer, and handling of stablecoins, Taproot Assets, RGB, and more, directly within Bitcoin’s ecosystem.
Minimal trust model: Security guaranteed through minimized trust in operators. Only one honest party is needed to keep the network safe (1/n trust).
Always open exit: Unilateral exit is always available in case of issues or whenever you wish. No permission or wait times needed.
Built to scale: High-performance infrastructure is designed to effortlessly support billions of transactions and scale with demand.
What Makes Up the Spark Ecosystem?
At the heart of Spark is a decentralized network of nodes working together to bring about secure, fast, and trust-minimized off-chain transactions. The protocol is designed to be modular and interoperable.
Here’s how all its parts fit together:
Spark Entity (SE): A Spark Entity is a group of operators that run the Spark core protocol and are responsible for operations necessary for signing and forgetting past keys.
Spark Operator (SO): A Spark Operator is an individual member of the SE that participates in multi-party signing and transfer of off-chain UTXOs.
Spark Service Provider (SSP): An SSP is a service provider that facilitates fast deposits, withdrawals, and Lightning transactions. Any number of SSPs can exist within one Spark.
Advantages of Spark to Different Participants
Spark isn’t just built for one type of user. Anyone interacting with Bitcoin in any way can benefit from a particular set of solutions that Spark offers for their user group.
For Everyday Users
Everyday users will benefit from Spark’s fast, near-zero-fee transactions, whether they’re sending bitcoin or stablecoins, without the need for channel management or other complications.
Through self-custodial services, they can hold onto their keys and funds. On top of that, Spark offers a better user experience than the current Lightning Network and statechain wallets.
For Developers
If you’re a developer, then you’ll appreciate simple SDKs and APIs that enable Spark integration into wallets and dApps. Meanwhile, the platform’s compliance-friendly setup alleviates fears over regulatory scrutiny and Bitcoin’s technical particulars, which means developers can focus on building innovative solutions.
For Businesses
Where businesses are concerned, Spark’s interoperability with Lightning and support for stablecoins bring numerous new opportunities in terms of global payments. Companies can settle transactions across borders, instantly, in any currency, and with ultra-low costs. It also provides the tools businesses need to develop custom wallets.
Bitcoin Use Cases Enabled By Spark
With Spark, new types of real-world applications and payment flows that weren’t feasible on Bitcoin before are now becoming a reality. Here are some of the most promising:
High-speed micropayments with zero fees
You can process transactions on Spark in under a second without paying gas or network fees (for Spark-to-Spark transfers).
Tokenized loyalty programs for Bitcoin-native businesses
Spark enables instant, zero-fee transfers of loyalty points between customers, while enabling them to maintain control over their loyalty tokens and allowing them to withdraw them to Bitcoin L1 at any time.
Non-custodial payment gateways with Lightning interoperability
Spark provides seamless interoperability with existing Lightning Network infrastructure, while giving users full control over their assets.
Efficient remittances with unilateral exit assurance
Spark enables you to exit to Bitcoin L1 without permission for everyday payments and global remittances, where on-chain bitcoin may be too slow or expensive.
Wallet-as-a-Service
Spark allows developers to build and deploy fast, low-cost, self-custodial, and Lightning-compatible wallets with instant, fee-free bitcoin transfers.
Stablecoins on Bitcoin
Spark can be used to issue, launch, and transfer stablecoins natively on Bitcoin in a compliant manner.
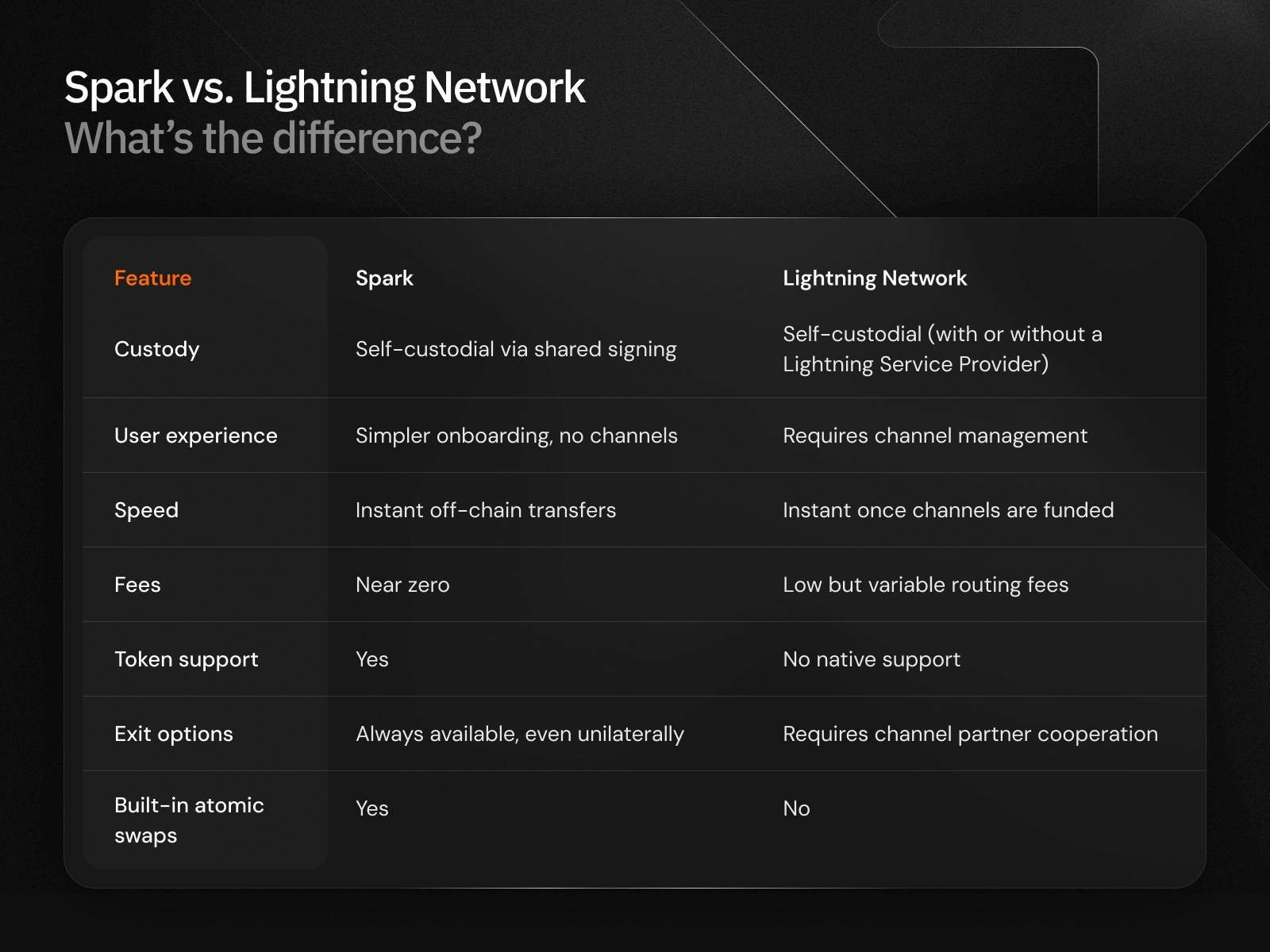
Spark vs. Lightning Network: What’s the Difference?
Although both Spark and the Lightning Network are Bitcoin Layer 2s focused on scaling, they take divergent approaches in terms of custody, user experience, token support, exit options, and other areas.
Understanding these differences is critical for anyone building or transacting on Bitcoin. Here’s an overview of how the two compare:
Xverse & Spark: A Seamless Gateway to Bitcoin DeFi
Spark will help bring mainstream-ready usability to the world’s most secure blockchain, including through self-custodial stablecoins, fast Bitcoin payments, and seamless swaps.





